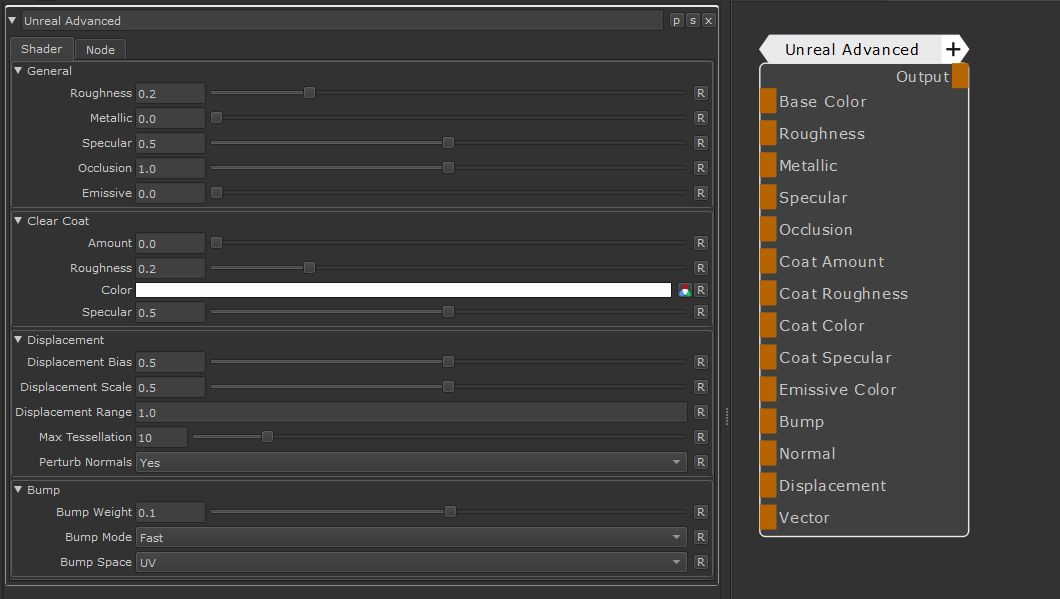
Determines the Diffuse Color of the Shader
Determines the Specular Roughness of the Shader.
When mapped with a Node, the Port overwrites the "Roughness" Slider within the Node Properties
Determines the Metalness of the Shader.
When mapped with a Node, the Port overwrites the "Metallic" Slider within the Node Properties.
At a value of 1.0 the Base Color of the Shader is used to drive Specular Color and Specular Reflectivity,
while the Diffuse Contribution is set to 0.
Determines the specularity and reflectivness of the Shader, when Metallic is set to 0.0.
When mapped with a Node, the Port overwrites the "Specular" Slider within the Node Properties.
Specular, also sometimes referred to as "Specular Level" is an abtraction of IOR, and only has an effect
of Dielectric (non metallic) materials.
Dialectric Materials commonly have a specular reflectivity between 0.0 and 0.08.
The Specular Level remaps these values to a range of 0 to 1, meaning its default 0.5 value corresponds to a specular reflectivity of 0.04.
The occlusion port can be used to supply a prebaked occlusion map to the shader.
The influence of the port can be controlled with the "Occlusion" Slider within the Node Properties.
Occlusion suppresses difuse and specularity in recessed areas.
Emissive Color adds a self-illuminating attribute to the shader.
Its intensity can be controlled via the "Emissive" Slider within the Node Properties.
Dertmines the amount of (clear) coating to apply.
When mapped with a node, the port overwrites the "Coat Amount" Slider within the Node Properties
Determines the Specular Roughness of the Coat Layer
When mapped with a Node, the Port overwrites the "Coat Roughness" Slider within the Node Properties
Determines the Color or the Clear Coat Layer
When mapped with a Node, the Port overwrites the "Coat Color" Field within the Node Properties
Determines the specularity and reflectivness of the Specular Coat.
When mapped with a Node, the Port overwrites the "Coat Specular" Slider within the Node Properties.
Specular, also sometimes referred to as "Specular Level" is an abtraction of IOR
Dialectric Materials commonly have a specular reflectivity between 0.0 and 0.08.
The Specular Level remaps these values to a range of 0 to 1, meaning its default 0.5 value corresponds to a specular reflectivity of 0.04.
Please note, a Clear Coat is always dielectric. It cannot be metallic.
Applies a bump to the shader
Applies a normal map to the shader
Applies a Displacement to the shader
Applies a Vector Map to the shader
 NodeGraph / Right Mouse Click / Nodes / Shader Network / Standalone
NodeGraph / Right Mouse Click / Nodes / Shader Network / Standalone